|
Homology modeling of Leishmania sirtuin and virtual screening for identification of novel anti-leishmanial compounds
Kiran V. M., Rameshwar U. Kadam and Nilanjan Roy
Homology model of leishmania SIR2 shed new light on the ligand binding features of this enzyme. Docking results could distinguish
between the reported inhibitory activity of nicotinamide and nicotinic acid. The model suggested that the nicotinamide binding
catalytic domain has several minor but potentially important structural differences compared to human SIRT2. These differences
could be exploited for designing anti-leishmanial compounds. Using docking study we have identified few putative sirtuin agonists,
these compounds are being screened for antileishmanial activity in Ali Ouaissi’s laboratory in France.
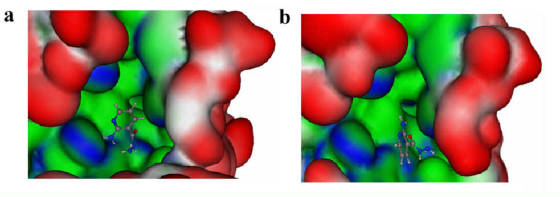
A inhibitor docked in leishmania (a) and human (b) sirtuin
GFA directed QSAR studies on antisirtuin activity of splitomicin analogues
Sumit Deswal, Pranav K. Singh and Nilanjan Roy
A comparative study of seventeen different classes of descriptors has been carried out to explain the Sir2 inhibitory activity
of splitomicin analogues. The 3D-MoRSE approach followed by GETAWAY approach best explains the variation in the activity amongst
all. However an excellent model is obtained when these descriptors are combined. Combined model is able to explain more than
88% variation in the Sir2 inhibitory activity of the compounds. The obtained models are being used for screening.
|
